In the previous year, we automated the Fedora downstream release process in Packit.
The first step of the release process, propagating the upstream release to Fedora,
is covered by the propose_downstream job.
This job updates the sources in Fedora, the spec file, and other needed files and creates pull requests with the changes
in the dist-git repository.
The downside of this job is that for its execution, users need to install Packit Service GitHub/GitLab app since this job reacts only to GitHub/GitLab release webhooks. However, the person who maintains the package in Fedora may not be the upstream maintainer and may not have admin access to the upstream GitHub/GitLab repository.
To cover this case, we came up with a new job called pull_from_upstream, which aims to update Fedora dist-git similarly
to propose_downstream, but is configured directly in the dist-git repository.
Let's now look at how to set it up and how it works.
Setup
Upstream release monitoring
pull_from_upstream job reacts to a new bug in Bugzilla about a new upstream version
of a project. The bug is automatically created by
Upstream Release Monitoring.
To enable the Upstream Release Monitoring:
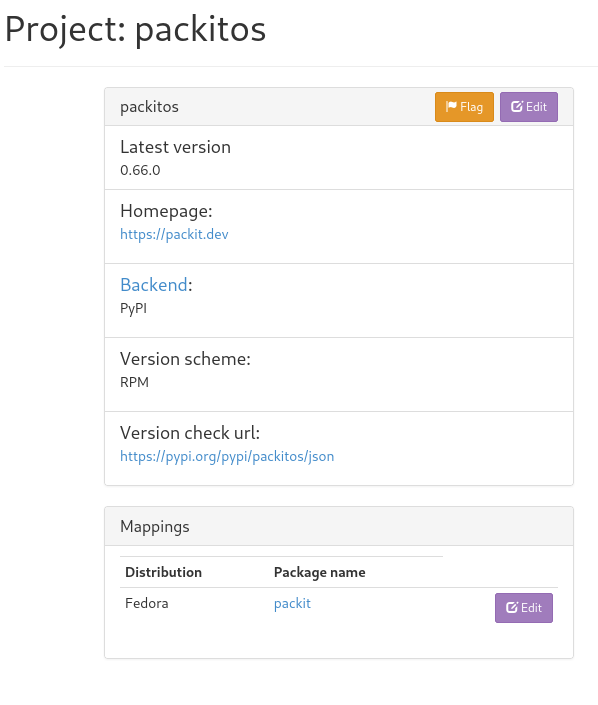
Add the upstream project (if it is not there yet) to Anitya and configure the mapping to a Fedora package:
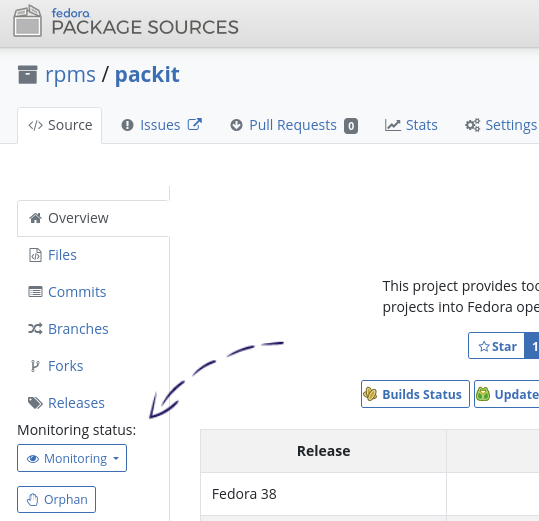
Enable the monitoring in the dist-git repository (Fedora Package Sources):
In Anitya, there are multiple backends you can configure the mapping for. Besides GitHub or GitLab, you can use e.g. PyPI, pagure, or many others. Also, be aware that there can be a delay in retrieving the new version, so the update to Fedora is usually not created instantly (e.g. for Python projects, it is better to configure PyPI backend rather than GitHub since the monitoring there is much less delayed).
Packit configuration
To automatically pull the upstream release as a reaction to the bug in Bugzilla, pull_from_upstream job
needs to be defined in the default branch
(rawhide) of the dist-git repository in the Packit configuration file (see
our documentation). The upstream_project_url
needs to be a URL pointing to a Git repository so that we can do git commands on it.
If not specified, upstream repository is not being cloned.
pull_from_upstream in action
Let's showcase the new job in action for the latest release of Packit itself.
As you can see in the Setup section above, the Upstream Release Monitoring is configured:
there is a PyPI project packitos in Anitya
with configured mapping to the Fedora package packit and the monitoring in the
packit dist-git repository is enabled.
We could configure the mapping in Anitya from the GitHub project directly instead, and it would work as well. Just be aware that
for each Fedora package, there can be a mapping only from one project.
In Packit configuration file, we have configured the job and related options:
upstream_project_url: https://github.com/packit/packit
issue_repository: https://github.com/packit/packit
copy_upstream_release_description: true
jobs:
- job: pull_from_upstream
trigger: release
dist_git_branches:
- fedora-all
- epel-8
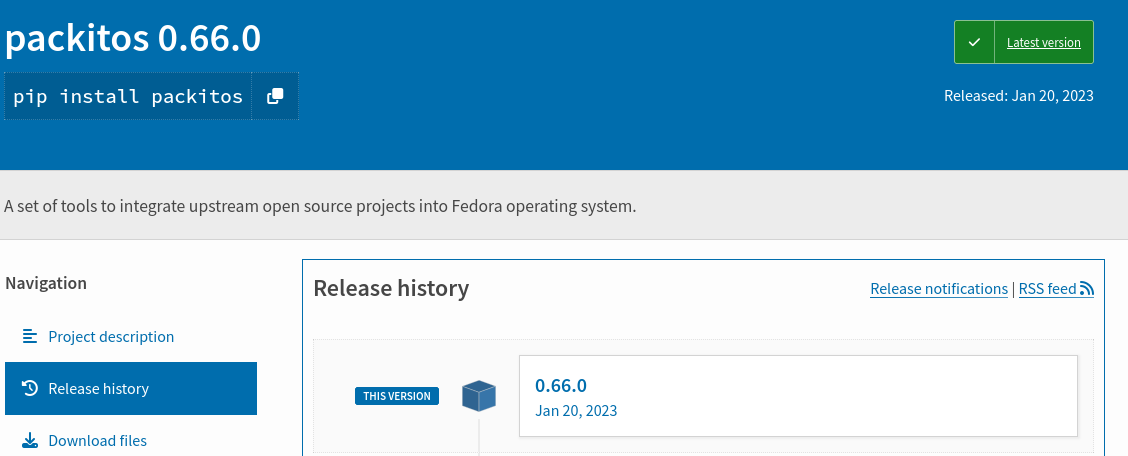
You can see that version 0.66.0 of Packit (packitos in PyPI) was released:
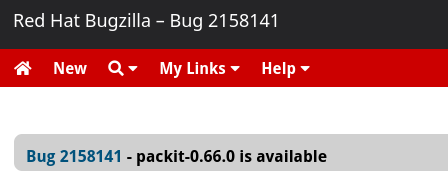
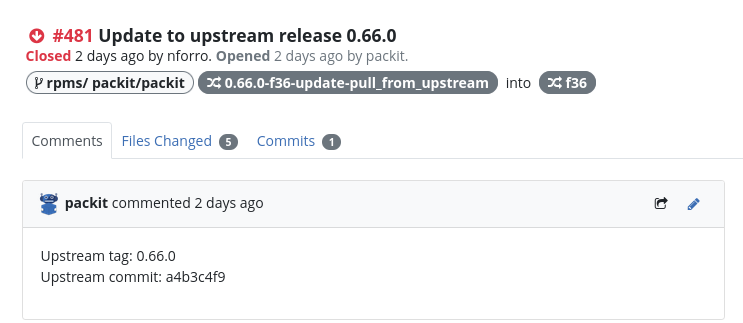
When Upstream Release Monitoring retrieved this new version, it created a new bug:
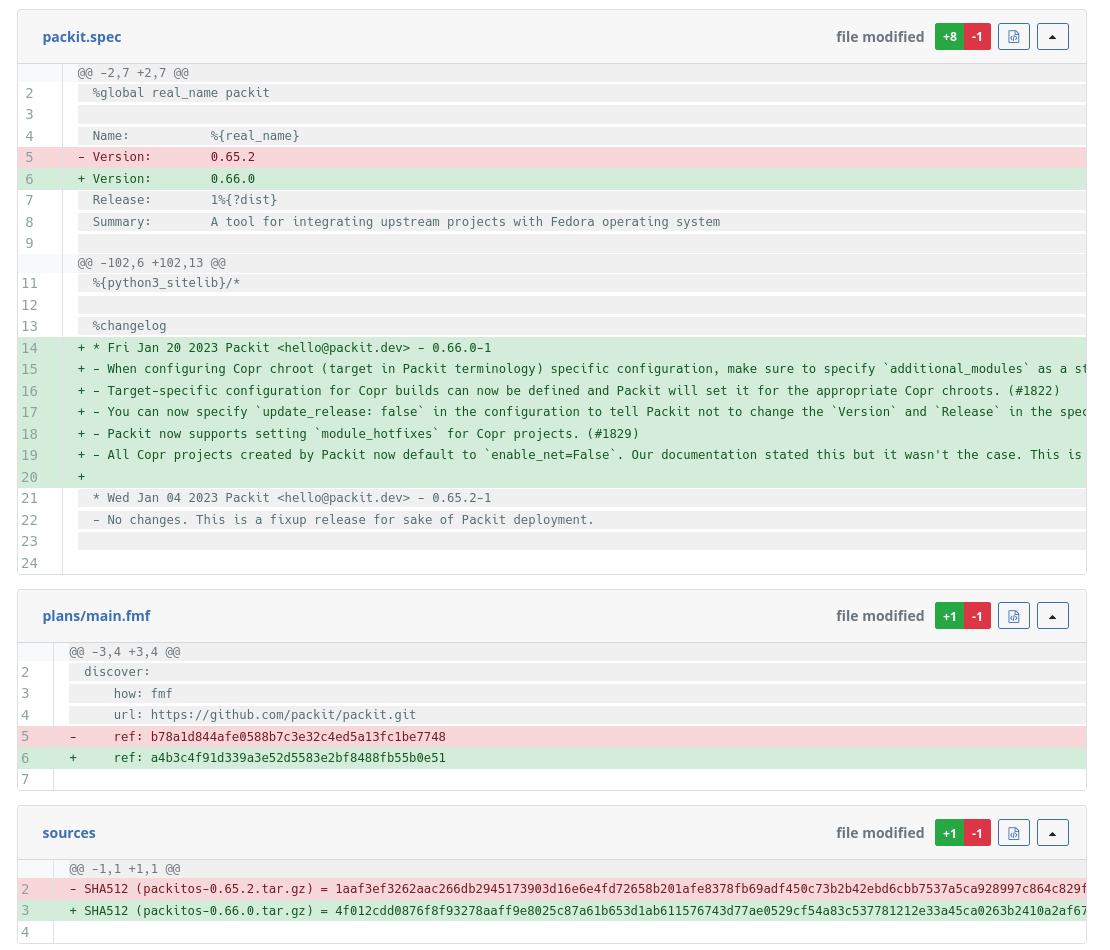
This triggered Packit, and after checking the Packit configuration in dist-git
and finding the pull_from_upstream job, this job was run.
Using the upstream_project_url from the configuration, Packit was able to get the needed information
from the corresponding GitHub release:
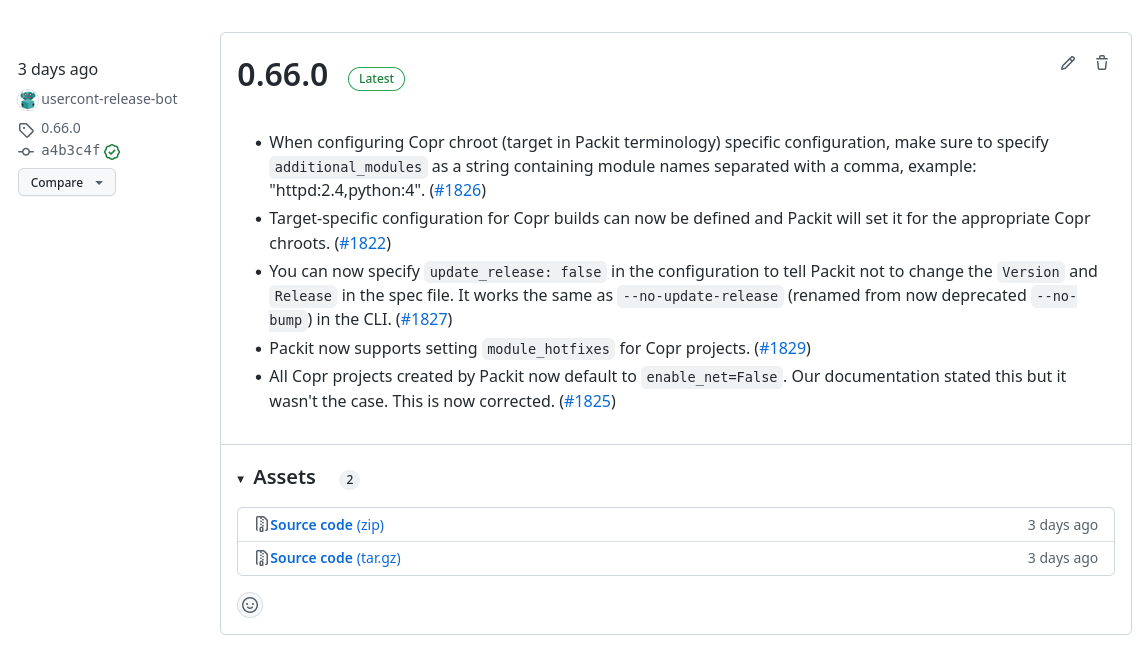
As a result, pull requests for configured branches were created.
Here is an example of one of the created pull requests and part of its content:
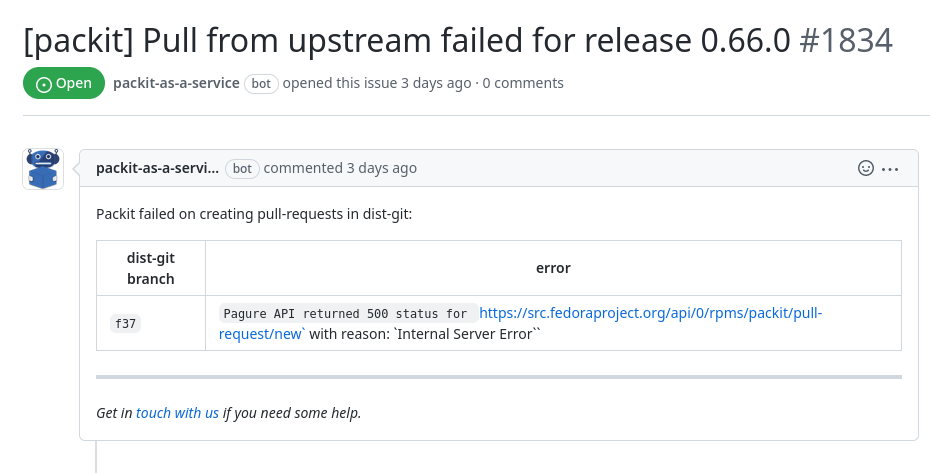
Since we have configured the issue_repository, we could be
also notified about errors:
It is now also possible to retrigger the job, see the details.
Also, if you need to do any change in the pull request, you need to locally fetch the source branch of the Packit's pull request and push it (with a fix) to your fork (as it is not possible to push to the branch created in the Packit's fork):
git fetch ssh://$USER.fedoraproject.org/forks/packit/rpms/$YOUR_PACKAGE.git refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/packit/*
git cherry-pick packit/$VERSION-$BRANCH-update-pull_from_upstream
Few words in the end
pull_from_upstream has just been implemented; therefore, we encourage you to help
test it out and make it perfect! There are still some limitations (e.g. regarding upstreams,
see documentation), which we are trying to resolve as soon as possible.
We believe this functionality
could be beneficial for maintainers of Fedora packages and could even be integrated further.
Any suggestions and feedback are welcomed
(see contacts).
If you are interested in details of customization of
the pull_from_upstream job and in the whole downstream automation, make sure to check out
our Fedora release guide as well!
